How get info about my IP address on macOS
Published on: 2020-12-30
IP addresses
Your home computer always contains two IP addresses. How local network works is described in picture below.
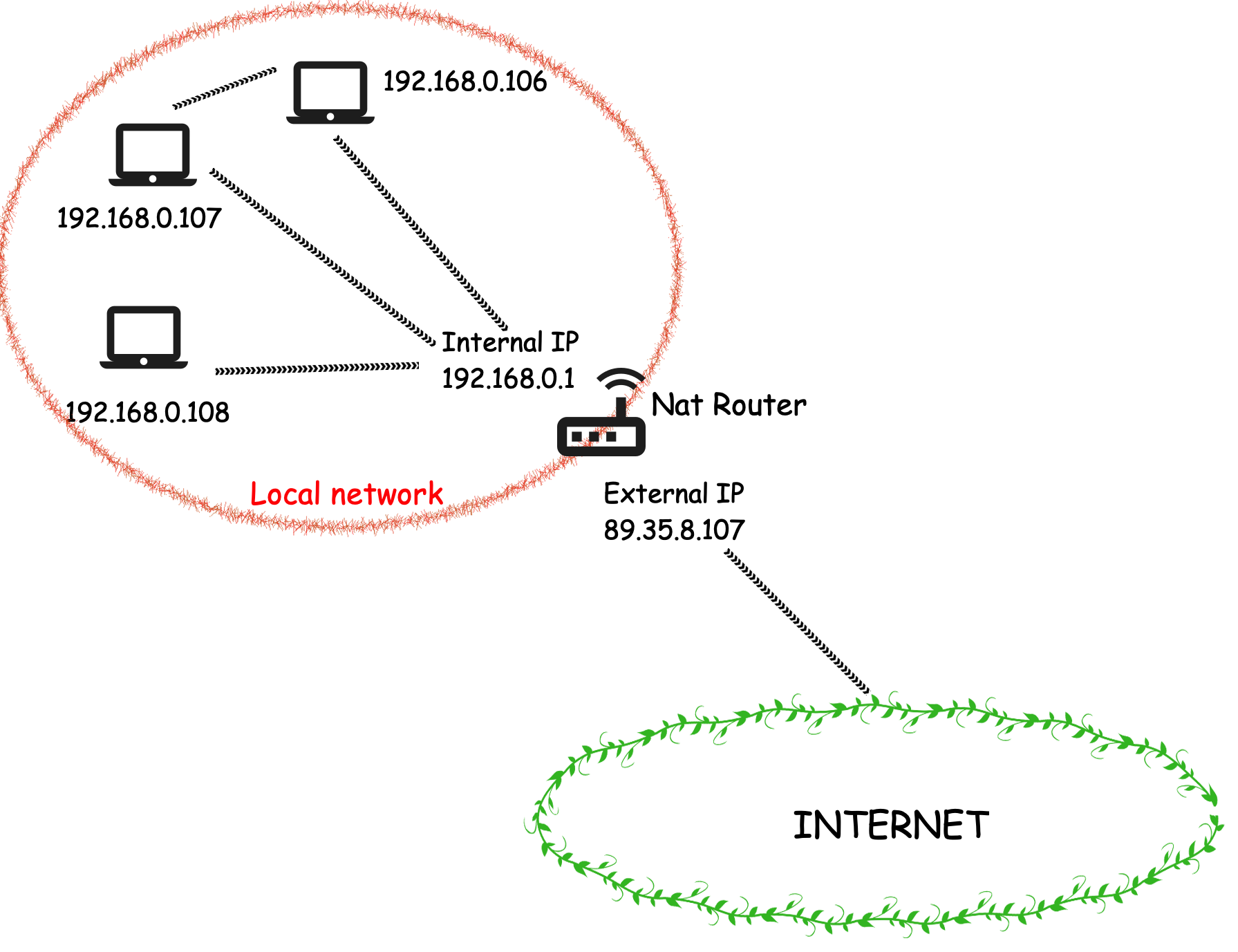
Icons used in image was created by Mithun Raj on freeicons.io. Thank you :)
Picture was created with Firealpaca
What two addresses I mean ?
There are:
- Internal (private) IP address - router interface when connects to local network
- External (public) IP address - router interface when connects to internet
For example (see picture above) - your laptop has internal IP address 192.168.0.106 but external address is 89.35.8.107
Our home Nat router allows connections in direction from internal to external network (internet) and not vice-versa unless is used technique called port forwarding. There is no direct connection between the Internet and a computer (except port forwarding).
So no one can not to connect to your internal IP address from internet. Only port forwarding allows device to get external IP address and reach this device from internet.
Internal (private) IP address
About Internal IP address is RFC 1918
we can set three types of private IPv4 address:
- Class A 10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255 (10/8 prefix)
- Class B 172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255 (172.16/12 prefix)
- Class C 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 (192.168/16 prefix)
Another type of private address is 169.254.X.X - it is IPv4 Link Local Address, it is used when we connect two computer with cable. There can occure a problem when we want this pc add local IP address with DHCP. This can not allocate IP addres with DHCP because this PC will dynamicaly allocate IP address by itself. So this function can be used if we do not have a DHCP server to automatically allocate IP addres for our PC. This address is not routable so we can not route this address by internet or another subnet. This address is automatically allocate to host whene there is no DHCP server.
Internal IP addresses use a special address range from a reserved non route-able address range. This range is same for every local network. Range is restricted for local usage. So the internal IP address ranges are blocked by Internet routers, you can not see them from internet.
Internal IP addresses have these schemes in most cases:
- 192.168.0.x
- 192.168.x.0
other schemes of private IP can be:
- 10.x.x.x is a 24 bit address block
- 172.16.x.x to 172.31.x.x is a 20 bit address block.
Your router has Internal IP probably as 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.0
Devices in your local network have these Internal IP addresses:
- PC 192.168.0.103
- TV 192.168.0.104
- Raspberry 192.168.0.105
- laptop 192.168.0.106
You can locally connect many devices to your router. But all of these devices will have only one External IP address of your router.
How to find out your internal IP addresses on macOS
There are two commands to check your IP:
- ifconfig
- ipconfig
When you prompt:
$ ifconfig
you should get output of all connections:
lo0: flags=8049<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 16384
options=1203<RXCSUM,TXCSUM,TXSTATUS,SW_TIMESTAMP>
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 0xff000000
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128
inet6 fe80::1%lo0 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x1
nd6 options=201<PERFORMNUD,DAD>
gif0: flags=8010<POINTOPOINT,MULTICAST> mtu 1280
stf0: flags=0<> mtu 1280
en0: flags=8863<UP,BROADCAST,SMART,RUNNING,SIMPLEX,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
options=400<CHANNEL_IO>
ether 78:bf:9b:c3:6b:02
inet6 fd60::18:1a2f:dabe:c1dc%en0 prefixlen 64 secured scopeid 0x4
inet 192.168.0.89 netmask 0xffffff00 broadcast 192.168.0.255
nd6 options=201<PERFORMNUD,DAD>
media: autoselect
status: active
en1: flags=8963<UP,BROADCAST,SMART,RUNNING,PROMISC,SIMPLEX,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
options=460<TSO4,TSO6,CHANNEL_IO>
ether 82:19:32:d2:ec:80
media: autoselect <full-duplex>
status: inactive
.
.
.
Your output will be different in view of your OS.
For Linux distributions you get these main variables:
eth[0-x]: ethernet interface, to connect with cablelo: loopback or local, when you use localhostwlan[0-x]: wireless interface, to connect with wifi
Output above is from macOS, there is some differents. See most of them below with explanation:
lo0: loopback (localhost)gif0: Software Network Interfacestf0: 6to4 tunnel interfaceen0: Ethernet 0 (ethernet), physical network connectionen1: Ethernet 1 (wireless), physical network connectionfw0: Firewire, IP over Firewire interfacevmnet0: Virtual Interface, interfaces are installed by VMware for network communication with virtual machinesutun0: Tunneling interface. Used for VPN connections to tunnel traffic or for software like Back To My Mack. creates VPN clientsllw0: Low-latency WLAN Interface. Used by the Skywalk system.ap1: Access Point. This is used if you are using your MacBook as a wireless host where you are sharing its connection.awdl0: Apple Wireless Direct Link. WIFI p2p connection for things like AirDrop, Airplay, etc. Also used for Bluetooth.llw0: Low-latency WLAN Interface. Used by the Skywalk systembridge0: Thunderbolt Bridge
If you want to get shorter output, where you will find your IP addresses easier, prompt:
$ ifconfig -a inet
It means show me all active and inactive connections and their inet. Inet means IPv4 and inet6 means IPv6. When you prompt ifconfig withou -a it shows only active connetctions see documentations or there is nice explanation to other usage for example how configure addresses to an interface etc.
inet: IPv4ether: MAC address
Other approach can be use command grep with ifconfig
$ ifconfig | grep inet
or
$ ifconfig en0 inet
If you want output only as your IPv4, then prompt:
$ ipconfig getifaddr en0
ifconfig VS ipconfig
ifconfig is used in UNIX OS and it means Interface Configuration. This command is the same as ipconfig, and is used to view all the current TCP/IP network configurations values of the computer
ipconfig is used in Microsoft Windows but ReactOS or macOS support this command. It means Internet Protocol Configuration. This command is used to view all the current TCP/IP network configurations values of the computer
When you dont want to use terminal for this quest you can read your internal IP address in you setting in macOS.
system preferences –> network –> Wifi –> advanced –> TCP/IP –> address IPv4
How to find all devices on your local network
For this purpose is the best choice to use tool called nmap
Tool nmap is not installed on macOS, so I recommend to instal via brew
$ brew install nmap
After installation you have to link the tool
$ brew link nmap
In my case I got a error
Error: The `brew link` step did not complete successfully
The formula built, but is not symlinked into /usr/local
Could not symlink nmap
/usr/local/share/.../.../man is not writable
brew link nmap
to fix this error use this command:
$ sudo chown -R `whoami`:admin /usr/local/share
whoami: is name your current user
chown: tool for change file owner and group, see man chown
-R: Change the user ID and/or the group ID for the file hierarchies rooted in the files instead of just the files themselves.
When link is complete then you can scan your local network with nmap
Command to scan your all active devices in your local network is:
$ sudo nmap -sn 192.168.0.0/24
It search all active connections with IP pattern 192.168.0.x. It is recommended to use as sudo because if you don’t use as sudo you received very basic informations.
-sn: Ping Scan - disable port scan, also called as quick scan in older version was-sP. This option tells Nmap not to do a port scan after host discovery. If you don’t use this option, the you get result with open ports./24: is referring to the subnet mask. It is CIDR format. /24 means that the first 24 bits of the IP address are part of the Network number (192.168.0) the last part is part of the host address (1-254).
Subnet-mask should be: 255.255.255.0
Network Address should be: 192.168.0.0
Broadcast Address should be: 192.168.0.255
Valid Hosts (Host range) should be: 192.168.0.1 - 192.168.0.254
Working for Host range:
28 - 2 –> 256 - 2 = 254
/24: is called as “slash notation”. It’s the number of bits that are specified. An IPv4 adress is 32 bits, divided up into 4 groups of 8 bits (n umbers from 0 to 255). 192.168.1.0/24 means any IP address in the range of 192.168.1.0 to 192.168.1.255. An IP address of 192.168.2.0/23 would be any IP address in the range 192.168.2.0 to 192.168.3.255 (notice the third number changes too) because it can have any value in the last 9 bits.
Also see the subnet calculation
External (public) IP address
External IP address is routable IP address. This address is assigned to you by your ISP. ISP has to assigned IP address to you from public addresses range which was assigned to your ISP by IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority).
IANA –> public addresses range –> ISP –> your external IP address
External IP address is used when you communicate with Internet.
You can notice that your External IP address change during the time. It is normal process because most of ISP gives you dynamic IP address. It means your ISP can change your External IP address how they need it. When you communicate with your devices from outside as a remote is good habit to have only one IP address without any change. For this purpose you need to get static IP address which is in most cases something extra and you have to pay for this service to your ISP.
Make from private IP address the public is done via NAT (Network Address Translation)
How to find out your external IP address
From internet
Check some service on the internet which will show you your external IP address. For example https://whatismyipaddress.com/ or just type to google my IP address and google will write to you…
Terminal
There is also web services which allow to use terminal. One of this service is https://ifconfig.me/, so when you prompt:
curl ifconfig.me
or
curl ifconfig.me/all
or
curl ipecho.net/plain ; echo